kubectl get pod -n kubernetes-dashboard | grep Evicted | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kubectl delete pod -n kubernetes-dashboard
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces | grep Evicted | awk '{print $2," -n ",$1}' | xargs kubectl delete podChanger l’éditeur pour nano
Linux
On Linux (Ubuntu, for example), typically the default command-line EDITOR is Vim. If so, no further action is needed to use the kubectl edit command. If you want to use a different editor, create an environment variable named KUBE_EDITOR with the value set to the path of your preferred text editor.
JAVA_HOME
1.1 Edit /etc/environment file with a text editor like vim or nano, need root or sudo.
Add JAVA_HOME at the next line, and points to a specified JDK folder directly.
PATH=”/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games” JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/adoptopenjdk-11-hotspot-amd64
source /etc/environment
echo $JAVA_HOME
Note
The new changes will disappear if we close the current session or reopen a new terminal because a new shell does not trigger the /etc/environment. Try to restart the Ubuntu or login again; the new changes in /etc/environment will apply automatically.
whereis nano
nano: /usr/bin/nano /usr/share/nano /usr/share/man/man1/nano.1.gz
sudo nano /etc/environmentKUBE_EDITOR="/usr/bin/nano"Ajout pod heimdall-node
deployement
La commande docker avec le filesystem preparé
docker run -d \
--name=heimdall \
-e PUID=1000 \
-e PGID=1000 \
-e TZ=Europe/London \
-p 80:80 \
-p 443:443 \
-v </path/to/appdata/config>:/config \
--restart unless-stopped \
lscr.io/linuxserver/heimdalltraduction en kubernetes deploy :
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: heimdallserver
namespace: default
labels:
app: heimdall
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: heimdall
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: heimdallserver
app: heimdall
spec:
containers:
- name: heimdallserver
image: lscr.io/linuxserver/heimdall
env:
- name: "UID"
value: "1000"
- name: "GID"
value: "100"
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: heimdall-http
- containerPort: 443
name: heimdall-https
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /config
name: heimdall-config
volumes:
- name: heimdall-config
hostPath:
type: DirectoryOrCreate
path: /usr/kubedata/heimdallserver/config
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: heimdall-svc
spec:
selector:
app: heimdall
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
targetPort: 80
nodePort: 32501
- name: https
port: 443
targetPort: 443
type: NodePortpuis on recupere le port d’exposition
kubectl get all --all-namespaces | grep heimdall
resultat le dashboard est accecible https://<master-ip>:32501

Exposer le Dashboard K8s
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48286170/how-to-access-canonical-kubernetes-dashboard-externally
Pour rendre accesible le dashboard Kurbernetes “form outside the machine” il est possible de modifier le type d’exposition de clusterIp a NodePort.
kubectl -n kube-system edit service kubernetes-dashboardremplacer “type: ClusterIp” par “type: NodePort”
en executant la commande suivante on recupere le port d’exposition
kubectl -n kube-system get service kubernetes-dashboard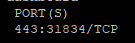
resultat le dashboard est accecible https://<master-ip>:31834

